& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the theory and development of computer systems that can perform tasks that would otherwise require human intelligence, such as pattern recognition from data; learning from experience; interpreting visual inputs; and recognizing, translating, and transcribing language.
In practice, AI is a way for humans and computers to work better together. In design and make industries, AI helps creative people do more with less by automating mundane and repetitive tasks and by cutting through the complexity of huge datasets to provide insights that may lead to new solutions.
AI works when computer systems apply logic-based programming to interpret data and automate actions with limited human input.
There are many subsets and types of artificial intelligence. For example, machine learning (ML) uses statistical data analysis for the model to improve its performance over time, in a sense learning from its mistakes and successes. As a subset of ML, deep learning goes further by analyzing data with artificial neural networks, which attempt to mimic human brain functions to find complex patterns in enormous data sets. Deep learning has made possible many AI innovations that are now common, such as computer vision (including facial and gesture recognition), voice assistants (Siri, Alexa), and speech-to-text transcription.
These innovations have already changed how people work and communicate and have made advanced technology available to more people than ever. As they develop, AI’s abilities will impact the global population on an even higher level. For example, deep learning AI contributes to analyzing medical images for disease detection and analyzing biological data for genome editing, discovering new medicines, and diagnosing diseases. In the global effort to build the infrastructure and housing needed for a growing population, AI can help plan for flooding, wind, noise and other conditions with predictive analysis, find efficiencies to free up people’s time and make manufacturing and construction more sustainable, and continue to assist workflows in new and more powerful ways.
Artificial intelligence, or AI, refers to computer systems that can perform tasks that otherwise would require human intelligence. There are, however, numerous types of AI for different purposes. The following are some of the most important types of AI, all of which can help people and computer systems to work better together.
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that lets computers “learn” from data sets without being explicitly programmed. Supervised learning ML learns from labeled data, such as images with metatags, whereas unsupervised learning ML works off unlabeled data. Either way, ML systems permeate modern life as a part of GPS maps, search and recommendation engines, spam filters, credit card fraud detection mechanisms, and much more.
Deep learning uses machine learning algorithms with biologically inspired logical structures called “artificial neural networks.” Deep learning is used for applications such as facial recognition and other types of computer vision, speech recognition for translating languages and transcribing spoken audio, bioinformatics such as analyzing DNA sequences and protein structures, and medical image analysis used to detect and diagnose diseases.
Generative AI is based on pre-trained, deep neural networks, which are capable of producing novel text, images, audio, video, and computer code. Especially when it comes to the large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Claude.ai, and many others that produce written outputs, generative AI’s messages are probable but unvalidated.
Generative design, not to be confused with generative AI, is an algorithmic process in which software runs precise real-world simulations to arrive at a set of optimal design solutions for a defined problem. Designers or engineers define their design goals, along with constraints pertaining to cost, materials, manufacturing methods, and performance and spatial requirements. The software can quickly generate numerous options that explore the possible permutations of the design requirements, simulating and learning from each iteration. Generative design solutions often but do not always employ AI.
Architecture and engineering firms are using AI to optimize buildings and sites for sunlight, wind, and noise conditions, while construction companies employ AI-powered robots for fast, accurate site mapping.
AI-powered robots and deep learning help manufacturers to avoid costly downtime by scheduling preemptive repairs, while generative design empowers designers to find optimal solutions based on parameter requirements and desired outcomes.
Artists can automatically manipulate scene data directly into Autodesk Maya using natural language text prompts thanks to the AI-powered Maya Assist tool.
Across industries, AI reduces tedious work, handles complex data crunching, and opens up new possibilities.
AI’s contextual assistance can enhance creative professionals’ creativity and exploratory capabilities by improving speed, accuracy, and breadth of thinking.
AI can automate workflow steps that traditionally required tedious and/or repetitive manual work, which can significantly reduce overhead and free up time to focus on more creative work.
When professionals face overwhelming amounts of complex data, AI features can sift through and understand what is really happening and give actionable insights.
With AI assisting in ideation and visualizing more contributors’ ideas, more voices are heard, and more projects can be launched, accelerating innovation.
Taking proper advantage of AI’s capabilities can lessen the gap between client expectations and design-and-make reality.
AI helps in specific areas of design and make. Autodesk Forma can maximize light in buildings and optimize sites for wind and noise conditions. Autodesk Fusion can automate 2D documentation while making manufacturing drawings interactive.
Ideally, AI will give users more time for creativity by decreasing the amount of tedious, repetitive chores. AI should augment and serve human creativity rather than replace it.
Generative AI has the potential to accelerate the visualization of concepts, leading to more ideas from more people. With faster ideation, teams can explore more possibilities and start more projects. Furthermore, AI features can help greatly reduce the gap between client expectations and design-and-make reality, boosting customer satisfaction.
Generative AI is already showing its transformative power for creative software in the AEC, design and manufacturing, and media and entertainment industries. Architects will be able to generate editable floor plans and easily import information from drawings into CAD projects. Construction IQ’s data analysis in the Autodesk Construction Cloud identifies risks and informs decisions on design, quality, safety, and project control priorities. Product designers can generate part assemblies for 3D CAD models. And in media and entertainment, AI generates 3D character rigging, making skeletal animation much faster.
Design and make firms are using AI to extend the reach of their work, whether that’s to the bottom of the ocean, to remote communities, or all the way to Mars.
UNTOLD STUDIOS
In addition to being the world’s first fully cloud-based animation and VFX shop, Untold Studios uses its own data to train machine learning models to accelerate repetitive tasks within disciplines such as character rigging.
EHAB KAOUD
In this interview and blog post, the ex-Ford Chief Designer and AI design expert shares thoughts on the AI design process, how to give generative AI feedback, AI’s limits, and how AI encourages exploration in automotive design.
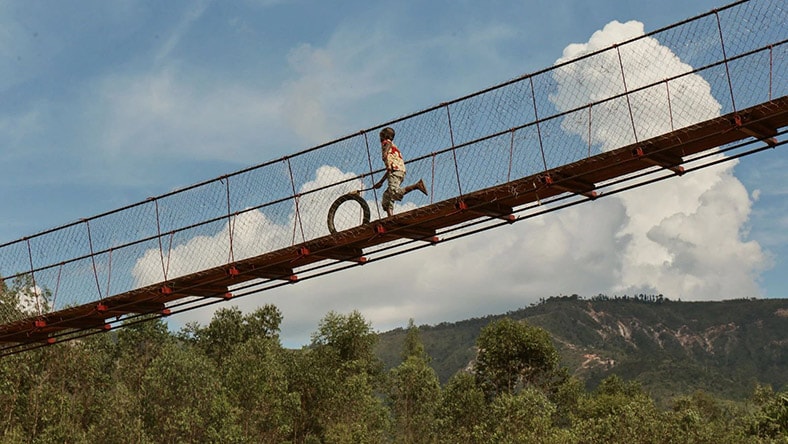
BRIDGES TO PROSPERITY
After creating design “presets” of trail bridges in Autodesk AutoCAD to connect rural communities to basic services, Bridges to Prosperity's AI and machine-learning geospatial data tool, Fika Map, remotely analyzes prospective sites so the nonprofit can easily scale up.
Image courtesy of Bridges to Prosperity
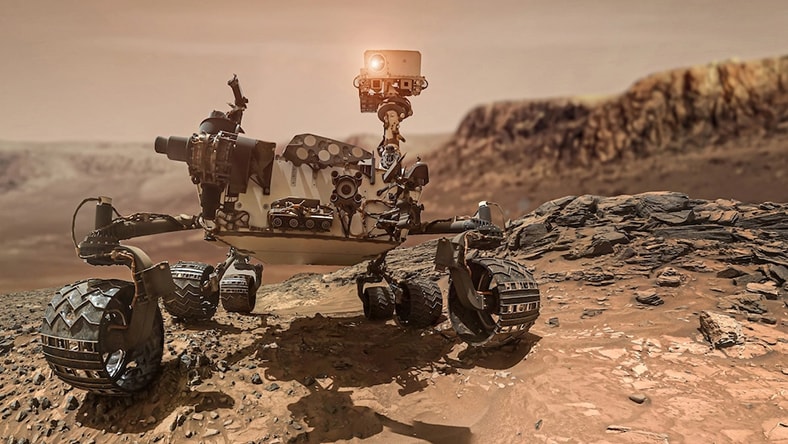
NASA
NASA used generative design to produce several parts for its EXCITE telescope and the Mars Sample Return Mission, taking advantage of the technology’s crucial benefits, such as designing for reduced mass.
Image courtesy of NASA
See how Autodesk AI’s innovations are already helping customers in AEC, design and manufacturing, and media entertainment do their work faster, better, cheaper, and more sustainably, with more capabilities being added by the day.
Learn how new approaches to collaboration and advanced technologies like AI and automation are transforming design and manufacturing work in this white paper from Harvard Business Review and Autodesk.
Culture changes in architecture, engineering, and construction—as well as the advancement of AI and automation tools—are generating returns for industry firms, according to this report from Harvard Business Review and Autodesk.
Five recent AI papers apply deep-learning AI to create 3D models from spoken words, predict how to join CAD parts, transfer style between 3D objects, and find different ways of reverse-engineering CAD models.
This Autodesk Fusion course starts designers on their generative design journey by introducing them to the mindset and workflow needed to succeed.
Quick videos and stories breakdown the process, benefits, and uses of generative design in the AECO industry, particularly for Autodesk Revit software.
Some examples of artificial intelligence include:
• Autonomous vehicles: AI interprets sensor data to make driving decisions.
• Chatbots: Customer service chatbots and large language model (LLM) AIs such as ChatGPT use natural language processing to answer questions.
• Virtual assistants: Voice-controlled assistants like Siri and Google Assistant, and their extended “smart home” systems like Apple HomePod and Google Home, use AI to understand spoken commands and to automate tasks.
• Recommendation engines: The people at Amazon, TikTok, and YouTube don’t really know what you want next; AI suggests things based on data including your behavior history and other people’s consumption.
• Health care: AI is used to assist in certain surgeries, detect diseases, formulate drugs, and personalize treatment plans.
Artificial intelligence is important for doing a number of things that people otherwise would not be able to do. For example, AI can analyze data at a volume and rate that far exceeds human capabilities, which has allowed people to use AI for example to diagnose diseases and to better predict traffic patterns and weather. AI’s data-driven insights can also help people make more informed decisions.
When AI takes over tedious and repetitive tasks, that can free up people and businesses to focus on more creative and nuanced problems. AI-based technologies such as voice recognition, text-to-speech, language translation, and others also make technology more accessible to people, especially those with disabilities.
While generative AI tools such as ChatGPT have become very popular, the most-used form of artificial intelligence is machine learning, a subset of AI where computer systems get better over time at making predictions based on large amounts of input data.
Examples of machine learning systems include IBM Watson, Nvidia Deep Learning AI, and TensorFlow.
Machine learning contributes to many technologies in use today, including search engines, autonomous vehicles, email spam filters, social media feeds, credit card fraud detection mechanisms, voice-recognition assistants, and recommendation engines.
AI is used in everyday life and has been implemented for years in a variety of ways that many people consider commonplace. For example, virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa use artificial intelligence for voice recognition.
Machine learning also pervades modern life. In transportation, GPS systems uses it to suggest the best route according to traffic data, and ride-sharing apps use it to match drivers with passengers and calculate trip times and prices. Recommendation engines for shopping, streaming video, and social media all use machine learning.
AI benefits health care through disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and more. AI contributes to security for example by identifying spam and phishing emails, detecting fraud in banking, and spotting unwanted activity from security cameras.
The disadvantages of AI can include high cost, job loss, lack of creativity and emotion, unpredictability, and ethical and privacy concerns.
AI’s high financial costs come from the amount of data, software, hardware, and human labor needed to maintain and repair them. Societal costs include the potential for AI to replace human jobs, especially jobs involving repetitive tasks and simple problem-solving. Another danger is that humanity could possibly become too dependent on machines.
Other societal concerns include AI acting with bias, discrimination, unfairness, and lack of transparency. Security and privacy concerns also abound, as AI collects huge amounts of data and is vulnerable to hacking, technical glitches, and human error.