& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Engineering simulation uses advanced software to visualize, analyze, and predict the result of processes and the behavior of 3D product designs while those products and systems are still in development. The insights gained from engineering simulation software help stakeholders make critical product design decisions in the digital phase, before moving to physical testing and prototyping—saving money, encouraging innovation, and accelerating time to market.
Many industries use simulation-based engineering to begin testing, validating, and predicting outcomes in the digital space well before entering the realm of physical testing and prototypes. Examples of simulation engineering are virtually limitless and apply to businesses of any size making products, structures, or systems based on 3D CAD models.
In the early stages of product development, simulation lets engineers rapidly access dozens of different design choices for functionality, performance, and durability. Before physical prototyping, simulation can save time and resources by testing virtual prototypes under countless conditions.
Simulating manufacturing processes before production can assess production methods and processes instead of learning through trial and error on physical machines. Engineering simulation can create efficiencies in quality assurance and maintenance by predicting and preventing potential errors in the product and by simulating the wear and tear of extreme conditions, predicting maintenance needs before they arise.
There are many ways that engineering simulation software can be used to gain insights, including:
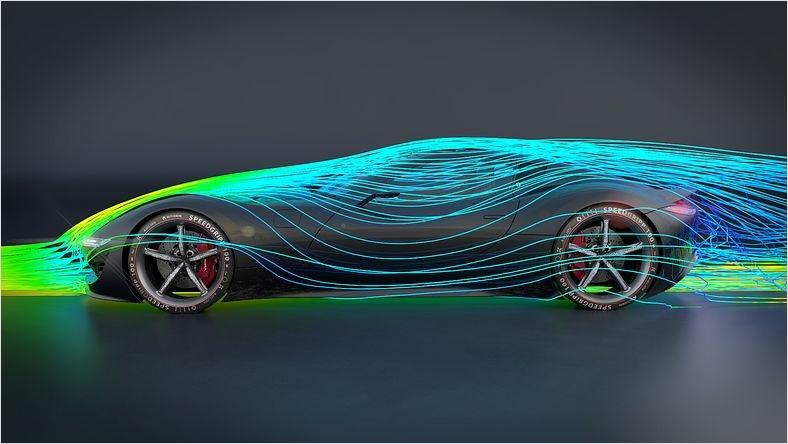
Mechanical simulation software can assess and analyze vehicle handling characteristics, impact stresses, aerodynamic performance, visual appearance, safety factors, fuel efficiency, and other crucial insights.
Structural stability, stress points, ambient conditions, and occupant comfort can be tested and optimized for construction projects of all sizes with modeling and simulation engineering.
Aerial vehicle handling capabilities, material properties, crash characteristics, and fuel efficiency can be tested and analyzed with engineering simulation software.
Engineering simulations can be used in electronic applications to test for and optimize key characteristics such as thermal loads, semiconductor performance, electromagnetic interference levels, and signal integrity.
Engineering simulations have applications across a product’s lifecycle and are used by a diverse range of professionals, including:
Designers can use modeling and simulation engineering to test design variations based on key factors; this helps them identify and develop iterations offering the highest performance and quality.
The ability to simulate new designs and concepts free from real-world constraints such as budget restrictions and short timelines helps researchers make great strides forward even with limited resources.
Whether it’s assessing risk, finding potential for optimization, determining manufacturability, or reducing cost, simulations help engineers do their jobs more effectively.
In the classroom, engineering simulations can help students visualize and understand the physical factors of different design and engineering choices.
Simulating product testing digitally rather than physically produces many tangible benefits, including:
With engineering simulation software, engineers can quickly analyze the performance of iterative design elements under various conditions to narrow down a short list of best options—all in the digital space, significantly shortening time to market.
The ability to test and validate product performance as 3D CAD models in engineering simulation software can greatly reduce the need for physical prototypes. Engineering simulation software also enables testing and validation in cases where physical prototyping is not possible, such as in large systems like buildings.
With engineering simulation software, engineers can test features and variations faster and more often than using physical prototypes. This allows them to detect and fix problems earlier in the design cycle, which has a positive impact on quality and performance.
Maximizing the use of engineering and mechanical simulation software reduces physical prototyping, shortens design cycles, enables the detection of engineering flaws earlier, and provides a central platform for collaboration—all of which heighten engineering’s efficiency and lower costs.
Because engineering simulation software can drastically reduce R&D costs and shorten design cycles, businesses can choose to pass some of those savings on to the cost of the product. Simulation software can also help find efficiencies in the materials used and the manufacturing process, leading to further product savings.
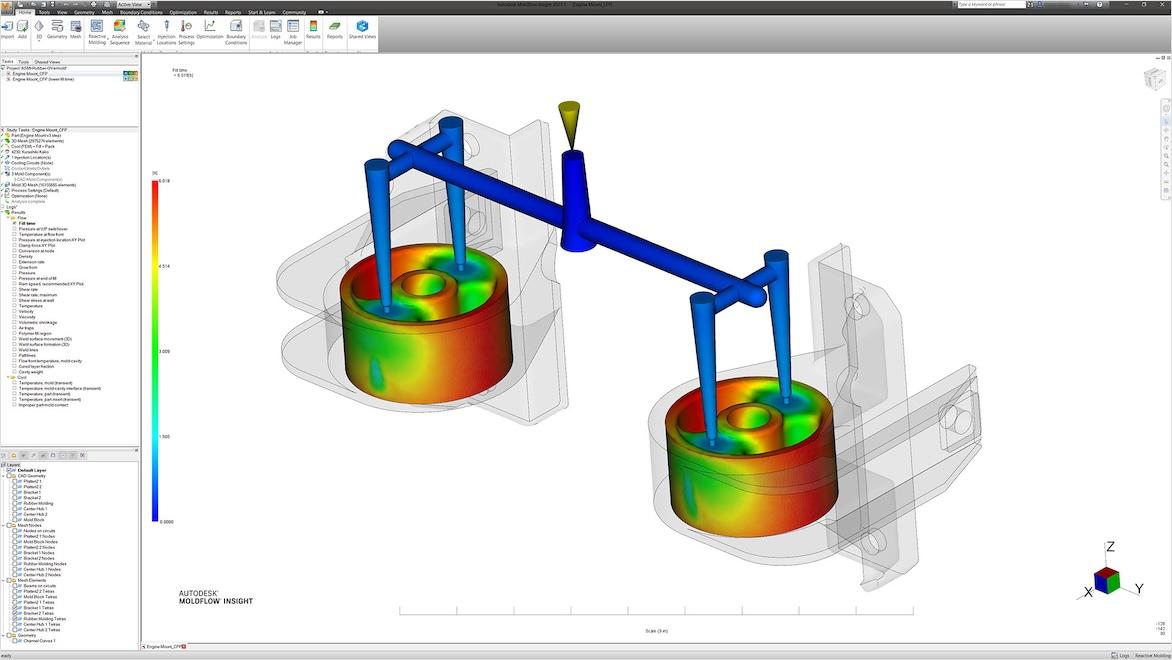
Engineering simulations have many purposes and may be specialized accordingly. Simulations in industrial engineering may focus on purely mechanical aspects or on the interactions between humans and machines. Thermal analysis engineering simulations analyze the heat transfer and temperature distribution between engineered systems so cooling and thermal management systems can be designed effectively. Mold-filling analysis is designed specifically to show how molten plastic may fill a mold during injection molding processes.
Computational fluid dynamics simulation and solid body motion analysis software. Available as CFD Premium and CFD Ultimate
Optimize part design and performance with unlimited cloud solves for generative design, FEA, electronic cooling, injection molding, and more.
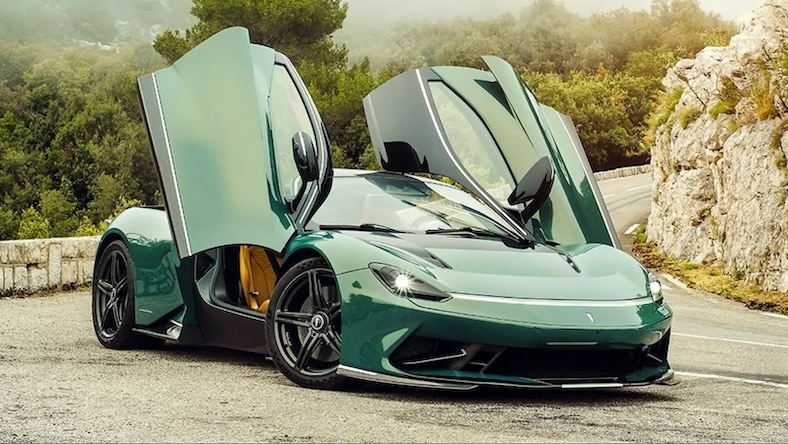
AUTOMOBILI PININFARINA
This revered Italian design studio may have gained inspiration from the natural world for its speedy Battista electric supercar, but visual simulations in the virtual world using Autodesk VRED sped up the design process significantly.
Image courtesy of Automobili Pininfarina
S-PLANE AUTOMATION
S-PLANE Automation conducted simulations early in the design process using Autodesk CFD and Autodesk Inventor software to smooth the meticulous workflow of making aviation electronics enclosures that manage flight control, power, and safety systems. The company lowered costs by reducing physical testing and prototyping while increasing collaboration and customer satisfaction.
Image courtesy of S-PLANE Automation
KAWAI PLASTIC INDUSTRY
This specialist in plastic injection molded parts trusted the Autodesk Fusion Simulation Extension to simulate and analyze the flow of plastics into a mold. By using modeling and simulation engineering, the company lowered trial injections by 25% and improved the quality and accuracy of its mold designs for the automotive and other industries.
Image courtesy of Kawai Plastic Industry
Today’s engineering and design workspace isn’t located in one place, it’s everywhere. Often, teams span different cities and even countries, and it’s important that they’re able to work together as if they were in the same room together. Autodesk Fusion is cloud-based, so all team members can collaborate on engineering simulations and other design aspects with ease. Cloud-based engineering simulation software also means that the performance load of the necessary operations is carried out by secure, remote servers rather than putting strain on your own hardware.
Get an overview of what engineering simulation software can do to increase productivity, make better products, and provide opportunities for insight and innovation in product design and manufacturing.
Take this professional Autodesk Fusion skill-building course and learn how to test, validate, and modify a design with mechanical simulation software before making a physical prototype.
Autonomous vehicles are like real-time simulation machines that use AI and simulation to predict traffic patterns, avoid crashes, and ultimately become better drivers than humans.
Find out how Autodesk’s finite element analysis (FEA) software simulates the effect of multiple real-world forces—like mechanical stress and vibration, motion, heat transfer, fluid flow, and others—on a product while it’s still in the 3D model phase. Then try the solutions for free.
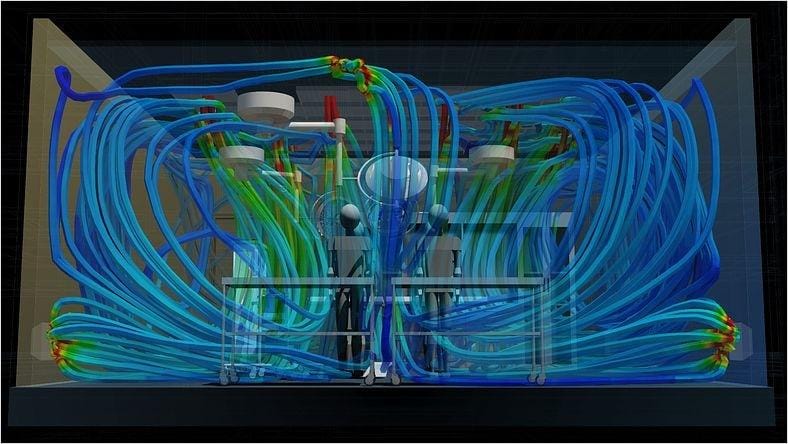
Learn how Autodesk CFD engineering simulation software predicts the behavior of liquid, gas, and air systems with computational fluid dynamics simulations. Gain motion, thermal, and other insights that can improve energy efficiency, reduce risk, and optimize cooling systems, lighting design, HVAC design, and more.
Explore the different applications of artificial intelligence that are helping enhance efficiency and improve product quality in the manufacturing industry.
Engineering simulation refers to the use of software to visualize, analyze, and predict the behavior of buildings, infrastructure, products, and systems in real-world conditions.
Engineering simulations can be created and customized for numerous engineering calculations. Examples include discrete event simulation (DES), finite element analysis (FEA), continuous simulation, process simulation, Monte Carlo simulation, and systems dynamics engineering simulations.
Discrete event simulation (DES) models a sequence of events in a system to show how the system responds over time. It’s commonly used to analyze and improve production systems. For example, Autodesk FlexSim models production, logistics, and people movement processes, and uses those models to visualize, analyze, and optimize the system.
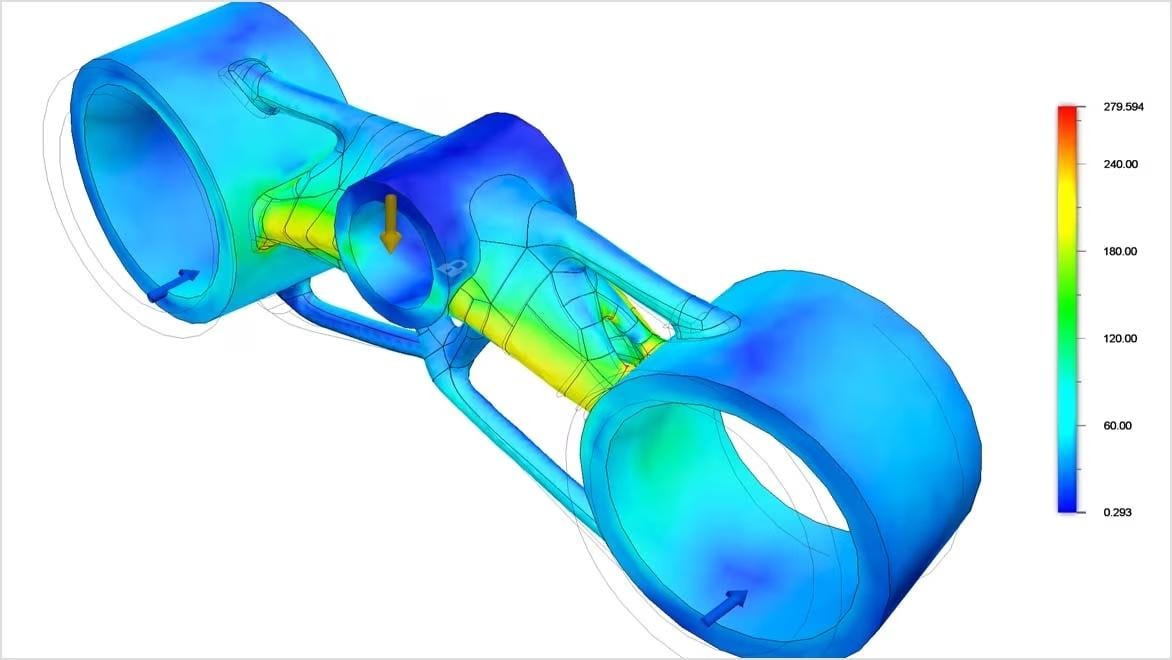
Finite element analysis (FEA) predicts how a product will react to real-world forces and effects like mechanical stress, vibration, and heat. It can be used to understand how a product will perform, including whether and how it may break or wear out.
Continuous simulation in industrial engineering deals with a continuously progressing state of being, such as the load stress of a tank filling with water.
In process simulation, the simulated process, such as the manufacturing of a product, can identify potential problems or opportunities for efficiency or quality improvements.
A Monte Carlo simulation looks at many random input variables to find the best output, such as matching a manufacturing process to the lowest cost for a level of demand.
A systems dynamics engineering simulation is quite complex and takes in longer-term data flows rather than static inputs like discrete events. System dynamics simulations are useful for revenue projections and supply chain management.
Engineering simulation is important because it allows designers and engineers to begin testing and validating products, buildings, and systems early and often in the development process. This saves time and costs, reducing risks and optimizing designs within engineering simulation software rather than with physical prototypes.
Mechanical simulation software from Autodesk provides a centralized, cloud-connected environment for multidisciplinary collaboration, innovation, and informed group decision-making.