& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Industrial engineering applies engineering principles and the scientific method to continuously streamline complex business systems, such as manufacturing, to improve quality while lowering costs. Relentlessly pursuing efficiency with regard to time, energy, materials, and money, industrial engineering can help any industrial company to work more productively and sustainably.
While industrial engineering is commonly known for optimizing assembly lines, the discipline applies comprehensively across all industrial systems, such as logistics and operations, always with the goal of increasing overall efficiency.
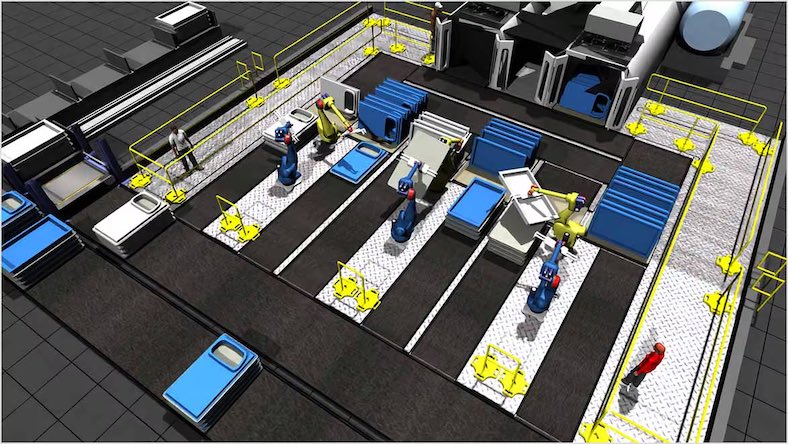
In manufacturing and production environments, industrial engineers utilize data from machines and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) at the component level to identify and rectify inefficiencies within assembly processes. This involves analyzing real-time data to optimize machine performance and interactions while also considering workforce ergonomics and safety. By harnessing this detailed data, engineers can achieve the core objectives of industrial engineering: enhancing process efficiency, anticipating maintenance needs, and improving overall productivity—all of which reduce lifecycle costs.
For logistics and supply chain management, industrial systems engineering can enhance the flow of inventory management to balance costs with demand forecasts, warehouse design that balances available space with handling time, and logistics related to transportation and distribution. Industrial engineers can design the supply chain for smooth procedures and resilience to disruptions, using manufacturing execution system (MES) software like Autodesk Fusion Operations to gain visibility and control over supply chain data.
Industrial systems engineering utilizes engineering principles drawing on physics, math, and even social sciences to inform decision making over the interconnected workings of industry: equipment, facilities, materials, energy, finances, and the workforce. Given these complexities, algorithms and machine learning from industrial engineering software can find automation opportunities—not just in assembly processes, but also in areas like scheduling and analyzing financial data.
The concept of industrial engineering appropriately coincides with the First Industrial Revolution and the advent of mass production. Decades later, Henry Ford provided a famous early case study by developing an assembly line that reduced automobile production time from 700 to 1.5 hours in 1913. Post-World War II, new industrial engineering theories for continuous improvement took hold, such as “total quality management” (TQM) in Western countries and “kaizen” in Japan. These movements applied to manufacturing and production and also to other aspects of industry, such as design, marketing, and business administration.
The goal of continuous improvement can benefit any business. And while industrial engineering was once most associated with manufacturing, many other industries use it, such as banking, health care, retail, transportation, and energy. Wherever complex systems and resource management can be optimized, industrial engineers can help.
Computer simulation continues to grow in power and utility. Simulation and digital twins of products, facilities, and systems can test functionality and predict outcomes, letting industrial engineers run thousands of simulated iterations for less cost than a handful of real-world tests. For example, 3D discrete event simulation like that offered in Autodesk FlexSim software, lets industrial engineers experiment with different factory designs and conditions risk-free, arriving at optimal solutions based on data.
As automation continues to expand in manufacturing and the other sectors where industrial engineers work, it will continue to take over non-value-added tasks from workers, letting them focus on manufacturing throughput and optimization. Automation can create efficiencies, but it comes with concerns about installation, implementation, maintenance, and more—challenges that industrial engineers must work to overcome. That’s one of the reasons the US Bureau of Labor Statistics expects industrial engineer jobs to grow 12% from 2022 to 2032, “much faster than average.”
The proliferation of machine learning and AI will undoubtedly affect every aspect of manufacturing and production. While AI will accelerate automation, it is still far from autonomous. Industrial engineers will work with AI to achieve further productivity gains.
With sustainability mandates in effect in many countries worldwide, industrial engineers are also in demand to develop sustainable practices. They can apply their skills to reducing the environmental impact of businesses’ energy and materials choices, as well as optimizing systems of energy production, distribution, and use. With industrial engineering focused on energy efficiency, lifecycle analysis, and resource optimization, industries will still have the ability to do more while using less.
Industrial engineers amplify their effectiveness with the right software, producing benefits at all levels, from production performance to system operations.
Higher quality standards can result from engineers’ optimizing products using dedicated industrial engineering software, which can build customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Whether it’s used for supply chains, cost management, or facility management, industrial engineering software helps maximize the production efficiency of entire systems, with real-time data insights.
Digital twins of products, machines, and entire manufacturing facilities mirror the functionality of their physical counterparts. Industrial engineers can run simulations in software like FlexSim to validate performance or test changes to designs or programming before enacting them in the real world.
Constant improvement in operational efficiency and product design from industrial engineering software leads to lower expenses and higher profits.
Industrial engineers are problem-solvers, and sophisticated software multiplies their ability to find solutions. This continuous focus on resource efficiency can result in less wasteful, more sustainable operations.
Get Inventor + AutoCAD + Autodesk Fusion + more—Professional-grade tools for product development and manufacturing planning.
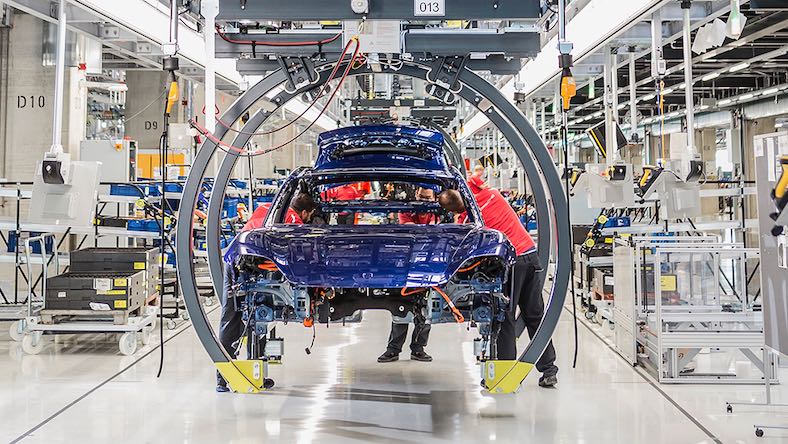
PORSCHE
To make its first fully electric sports car, the Taycan, Porsche industrial engineers used digital factory planning to build a thoroughly modern, flexible facility in Stuttgart, including driverless transport systems and a holistic approach to resource and waste management.
Image courtesy of Porsche AG
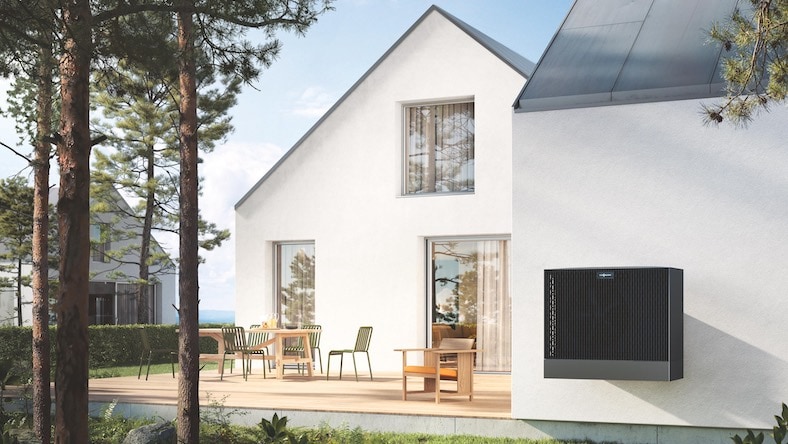
VIESSMANN
To meet the surging demand for its heat pumps, Germany’s Viessmann designed a new smart factory with digital factory planning and industrial engineering software to automate production, assembly, and logistics processes, as well as extended reality (XR) tools for visualizing the factory’s digital twin.
Image courtesy of Viessmann
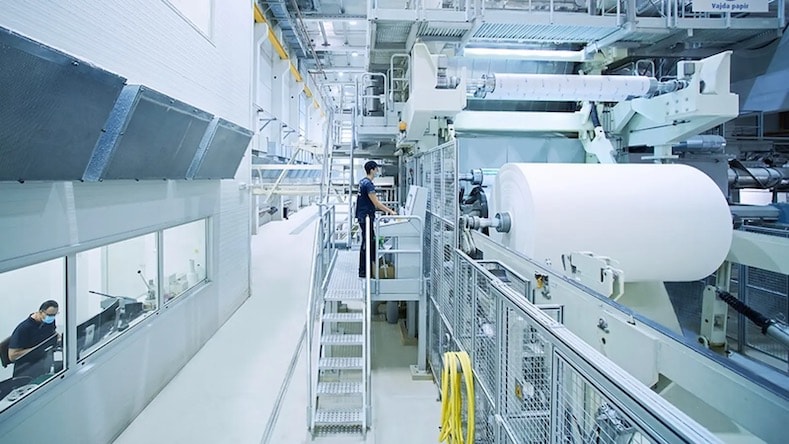
ANDRITZ
Industrial engineers at Austrian company ANDRITZ design highly networked plants and machinery systems for the pulp and paper, hydropower, metalworking, and other industries. Their production line for Hungarian paper mill Vajda Papír integrated 3D modeled digital twins of every component, with sensor data and AI working to monitor the entire factory to avoid downtime and optimize efficiency.
This quick video explains how the manufacturing industry is on the cust of being able to make more with the same number of people and less impact on the planet, thanks to AI-assisted, cloud-connected industrial engineering software.
Learn about the technologies and benefits of smart manufacturing—which digitizes the factory floor with robotics, AI, and sensor data, as well as digitizing designs and sales—and how industrial engineers can use it to increase productivity, competitiveness, and resilience to disruptions.
Industrial engineers working in the building industry and striving for sustainability can look to industrialized construction—the scalable application of lean manufacturing techniques to the design-and-build process—to cut down on material waste and achieve all forms of resource efficiency.
Creating a digital factory in deliberate phases allows industrial engineers to customize production, achieve greater agility and competitive edge, and address waste reduction and other environmental concerns.
Read up on AI proliferation in manufacturing with the rise of ubiquitous sensor data, autonomous systems, robots, factory digital twins, and industrial engineering software that emphasizes simulation and generative design. The use of AI in manufacturing boosts speed, precision, and quality control.
The infusion of machine learning AI into factory robotics has helped industrial engineers make manufacturing more agile, customer focused, efficient, safe, and profitable. Operations can adopt machine learning robotics incrementally and immediately see differences while making assembly lines more configurable.
The future of industrial engineering will continue to find greater efficiencies and improvements to workforce conditions through a growing reliance on interconnected Industry 4.0 technologies such as robotics and AI/machine learning, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT) and edge computing, cloud computing and big data analysis, and other digital transformation technologies. Strengthening supply chains to be resilient to unforeseen fluctuations will also be important.
In addition, the trend of industrial engineers focusing on sustainability by improving eco-friendly processes, reducing waste, and encouraging social values will continue. Industrial engineering in manufacturing will play a key role in working toward a truly circular economy, where all products are durable, repairable, reusable, and/or recyclable.
Industrial engineers use many specialized tools to continuously improve systems and processes. Starting at the top, facility layout design software lets industrial engineers practice digital factory planning to optimize the available space. Industrial robotics and other automated machinery streamline production, enable precision manufacturing, and reduce drudgery labor. Using integrated CAD/CAM/CAE software that’s cloud-connected to production hardware allows industrial engineers to dial in improvements to automated systems quickly based on data analysis.
Other important industrial engineering software tools include simulation software that lets engineers test complex processes virtually, yielding faster and less expensive insights, and manufacturing execution system (MES) software like Fusion Operations, which helps track processes and ensure quality control. Connected platforms like Autodesk Platform Services (APS) give industrial engineers access to data from multiple business systems and data sources via APIs and web services.
Industrial engineers work to continuously improve productivity, efficiency, and performance across industries. They do this by focusing engineering principles on systems such as supply chains and logistics; quality assurance, validation, and risk aversion; facility design and layout; workforce planning and safety, and process optimization.
Within each area, industrial engineers combine their technical know-how and problem-solving abilities with the complex data analysis and process simulation that’s possible using advanced industrial engineering software tools.