& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Injection molding is a method for manufacturing high-volume parts with plastic materials. Due to its reliability and flexibility in design options, plastic injection molding is used in many industries, including packaging, consumer electronics, automotive, medical, and many more. Injection molding is typically for manufacturing plastic products using thermoplastic or thermoset polymers but is also used in some metal injection molding applications.
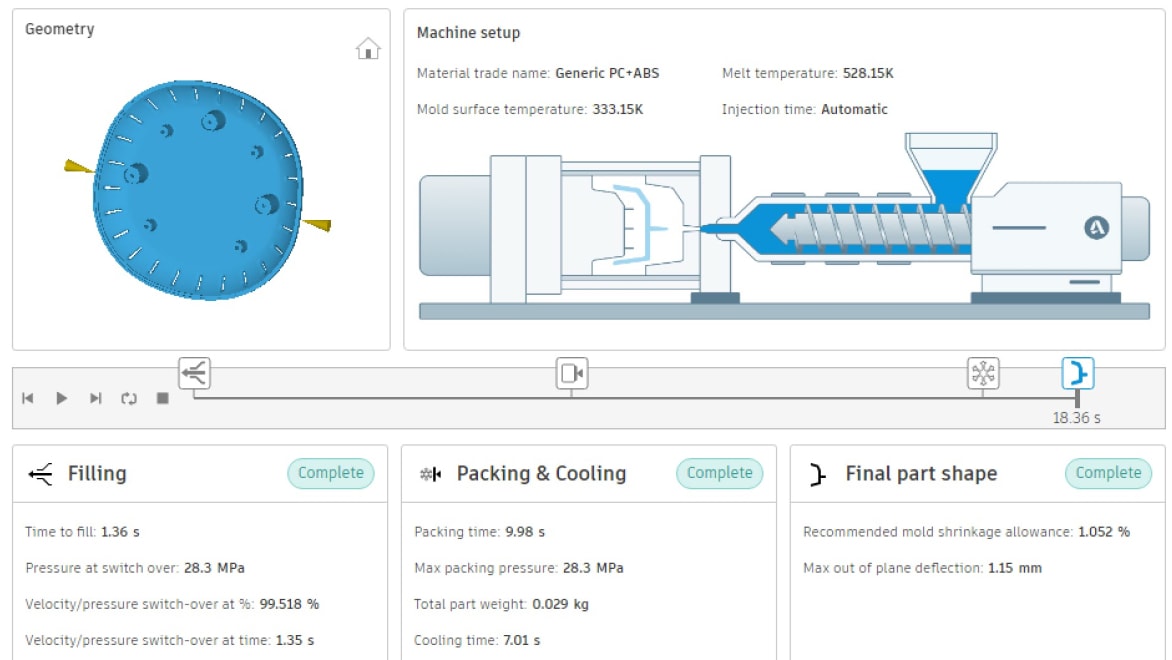
The plastic injection molding process uses a machine divided into clamping and injection units. A metal mold containing a cavity matching the desired part’s geometry is clamped into place on the machine. Next, the injection unit melts plastic pellets and injects the molten plastic into the mold at a very high pressure. Depending on the features of the part and the type of plastic, there may be a holding period when the plastic-filled cavity is held under pressure to ensure that it forms correctly.
The mold has cooling channels that help uniformly cool the material. During the cooling period, pressure is released to help with cooling. Finally, the clamping unit is released and mechanisms eject the part from the mold, triggering the process to then repeat. Injection molded parts may need additional finishing steps, such as removing molding aids like plastic sprues or runners, polishing, or assembly to other components.
Autodesk’s Moldflow analysis software can help you get the most out of the process and achieve the best results through plastic injection simulation.
The traditional plastic injection molding process can be modified to include processes that help to enhance part quality and part design flexibility.
Molding with thermoset materials requires heat or chemical means to cure the material. It uses a similar process as thermoplastic injection molding but may have a hot mold instead of cold one. It may also require a cure time instead of cool time, with the mold closed.
Overmolding is a plastic injection molding process where one material is molded on top of another. This includes molding over part inserts (such as a metal thread). An example of this is a hard plastic part that has a softer (or rubberlike) component—think of a hairbrush or battery-powered drill with a soft handle.
After injecting plastic into the mold cavity so it only fills a portion of the cavity, an inert gas is introduced, at high pressure, which results in an air pocket in the center of the part. This reduces part weight while achieving a high-quality surface finish.
This process involves the injection of two different materials using either the same or different injection locations. One use case for this is a product with a stiffer material as a base and a softer, more flexible material on the exterior to withstand a wider range of performance applications.
In this process, a physical blowing agent, chemical blowing agent (CBA), or mold core-back process is used to trigger the foaming of the polymer inside the mold. This is a way to reduce the weight of parts while keeping the structural integrity of the part—thus, it is often used in automotive components.
This forming technique is for producing small components using powders, typically ceramics (CIM) or metals (MIM), and binding agents, typically polymers. The material follows a similar process as traditional injection molding.
Plastic injection molding manufactures high quantities of parts faster than other manufacturing methods like machining or 3D printing. High accuracy and automated processes result in identical part creation, promoting low labor costs. Customization allows flexibility in part design (for example, molded-in inserts) and material properties (such as color, clarity, strength, and flexibility).
Part designers, mold engineers, and other manufacturing stakeholders run into different challenges with plastic injection molding, which ultimately affect part quality if they are not caught in the early design stages. The upfront investment in injection mold tooling can be thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, which means extra care is needed to prevent having to adjust or rebuild molds.
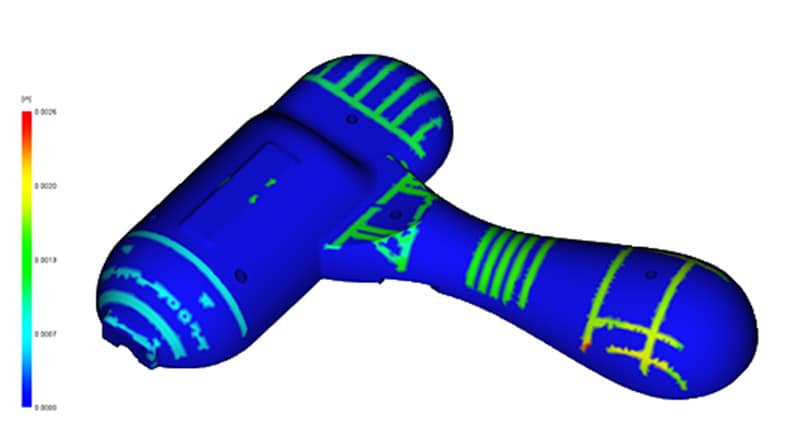
Some examples of molding and process challenges include material variations, weld lines, sink marks, warpages, long cycle times, and incomplete cavity filling. By using plastic injection molding simulation software such as Autodesk Moldflow or Autodesk Fusion Simulation Extension, you can eliminate many of these challenges before they become problems.
Autodesk’s Moldflow Insight software features an application programming interface (API) that will allow automation for many everyday operations and tasks. You can save time and take the hassle out of plastic injection simulation with custom report generators, macros, and more.
Incorporating new elements into your injection molding workflow and processes can take a lot of trial and error. Fortunately, you can download a free trial of Moldflow Adviser injection molding software without any risks. The trial lasts for 30 days, so you’ll have plenty of time to try out its plastic injection simulation features to see if they work for you. The trial gives you full and unrestricted access of Autodesk’s Moldflow Adviser analysis software; if you decide it’s not for you, just turn off automatic renewal before the trial period ends.
There are two versions of Moldflow to choose from. Moldflow Adviser is designed for engineers who work in injection molding design and helps optimize designs for manufacturing and usage. Moldflow Insight is good for analysts and planners and features access to a pre-loaded injection molding database of mold and part inserts, automated design of experiments, and analysis sequences.
Mechanical engineers and part designers who are finalizing their product designs in Autodesk Fusion may instead opt for the Fusion Simulation Extension. This product includes an injection molding simulation that shows how product features may influence part quality and provides suggestions for how to minimize or eliminate those concerns.
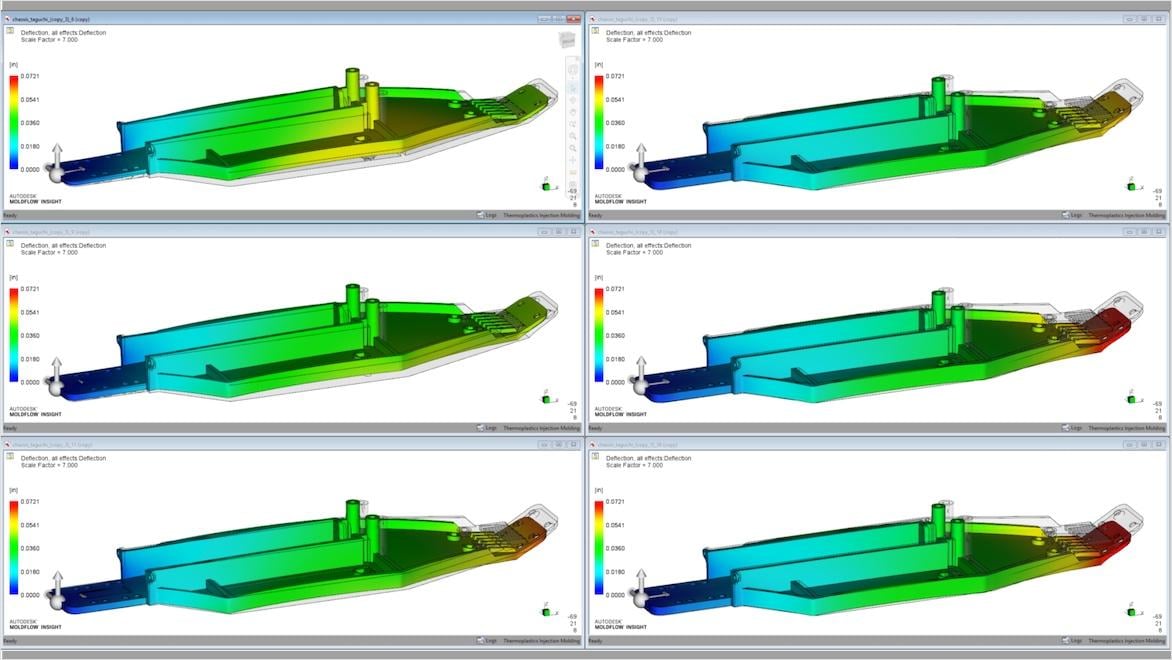
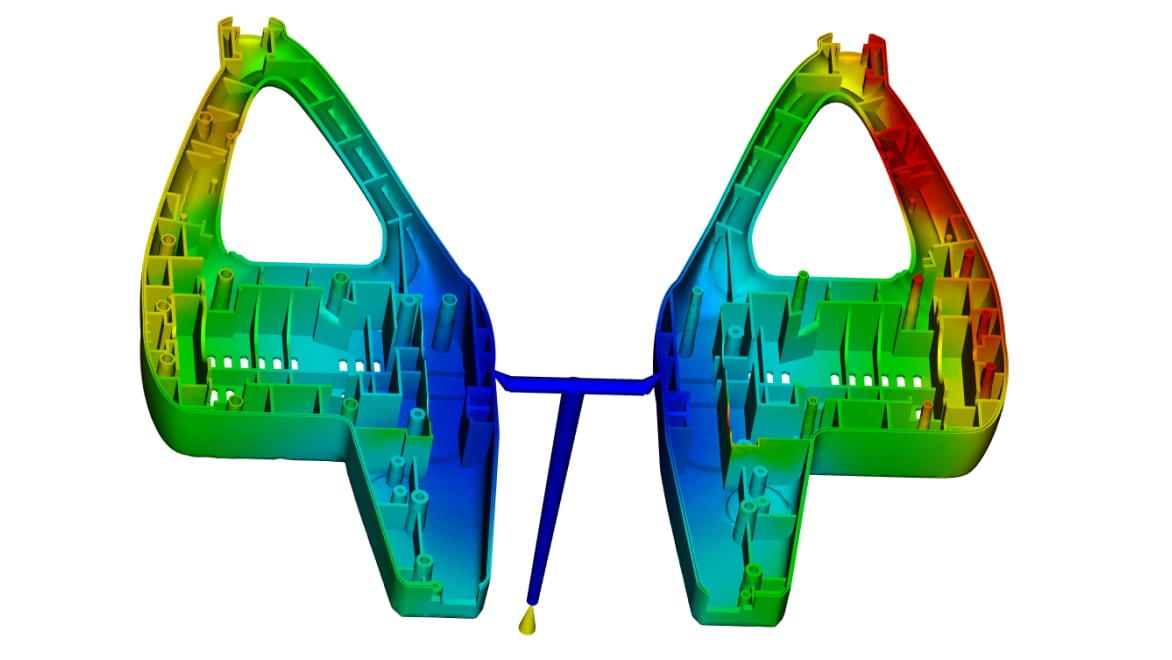
Molding simulation can help designers and engineers understand risks early in the design process, enabling them to address these before becoming fully invested. Simulation software gives engineers, mold makers, and other product design and manufacturing professionals accurate digital prototyping solutions and helps bring better products to market faster.
Injection molding simulations can be paired with other simulation tools, including mechanical stress, vibration, motion, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and multiphysics. Software like Autodesk Fusion Simulation Extension combines several of these simulation tools, providing a fast, accurate, and innovative approach to solving the most challenging design problems.
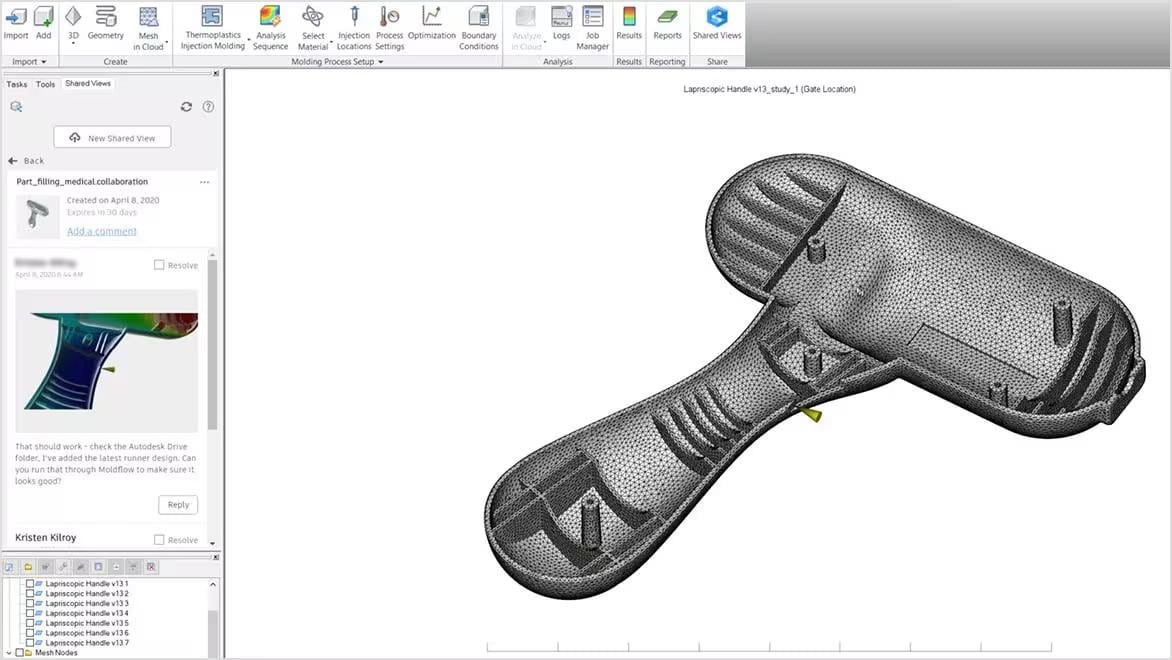
Autodesk's plastic injection simulation software makes it easy for teams to work together. With Autodesk Moldflow and the Fusion Simulation Extension within Autodesk Fusion, you can collaborate through shared views, sharing results, feedback, design recommendations, and more via cloud-connected devices, even if the team is spread across multiple continents. Team members can also import CAD files into the injection molding software directly, without the need to convert them for simulation. All users can view results side by side for comparison, allowing methodical improvements of injection molding processes.
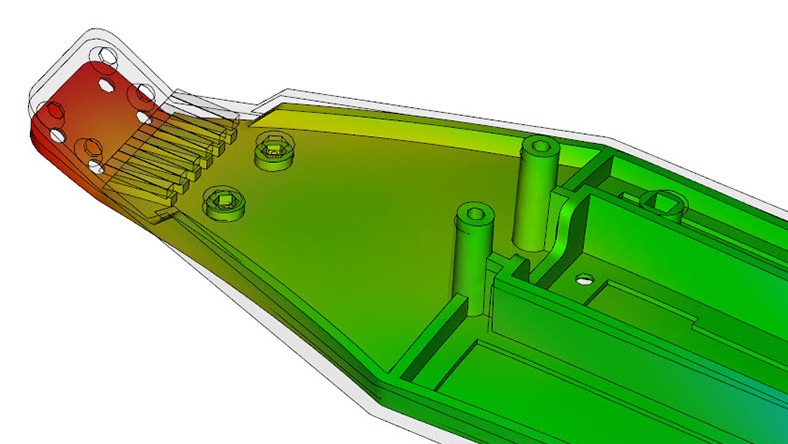
Analyze fill patterns and the effects of geometry and process setting changes, such as sink marks.
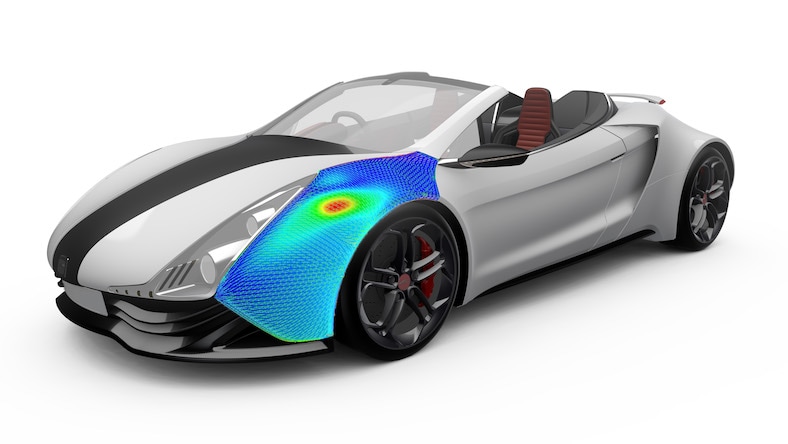
Investigate the causes of warpage, then examine options to minimize or correct part deflection.
Analyze and compare advanced materials for lightweighting efforts, such as with automotive components.
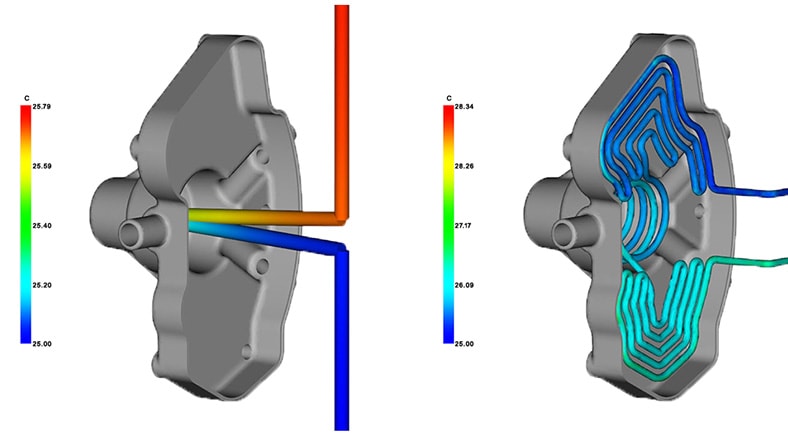
Predict part cooling efficiency. Experiment with conformal cooling or induction heating options before investing in costly molds.
Optimize part design and performance with unlimited cloud solves for generative design, FEA, electronic cooling, injection molding, and more.
CAD modeling software to prepare molds, dies, and other complex parts for manufacture—available as Standard, Premium, Ultimate
Explore simulation through use cases, validation reports, and technical papers from our team of experts.
Interact directly with current Moldflow Insight users and the Moldflow product team.
Read through various support articles covering injection molding concepts, simulation how-tos, and troubleshooting.
Keep up to date with molding simulation through engineering-focused blog posts.
Interact directly with current Moldflow Adviser users and the Moldflow product team.
Watch and read how Moldflow simulation has directly impacted product design and manufacturing.
Learn how our product innovation platform lets you more effectively design products and manage product lifecycles.
Explore manufacturing software that may help you machine, print, inspect, and fabricate better quality parts, faster.
Absolutely. Manufacturing a prototype, testing it to see where problems lie, iterating the solution, and building a new mold cost time and money. Instead, you can test your 3D design in simulation software and find potential issues before you build a single prototype.
Moldflow simulations can provide an extra step toward molding sustainably by providing insights into your material’s environmental impact.
No matter what CAD platform you use, look for injection molding simulation software that connects to it seamlessly so it’s easy to bring your design into its environment. The fewer CAD file conversions needed, the higher the likelihood that your simulation will be accurate and free from modeling errors.
Such interoperability should ideally include the ability to update or rerun simulations easily and on the fly as you make changes to your geometry.
If you work with a complicated part or process, or you need to simulate multiple materials or mold iterations all at once, look for software with remote server and/or cloud connectivity, which will give you the capacity to run simulations concurrently.
Most importantly, your injection molding simulation software should answer the questions you are looking to answer about your finished part, like:
Software solutions for plastic injection molding include Autodesk Fusion Simulation Extension, Autodesk Moldflow Adviser, and Autodesk Moldflow Insight. The Autodesk Fusion Simulation Extension costs $200/month if paid monthly or $1,600/year if paid annually and requires an active Autodesk Fusion subscription.
There are different Moldflow injection molding simulation product versions depending on your needs. Review your options by visiting the Moldflow website, and work with your official Autodesk reseller/partner for pricing.
An Autodesk Flex subscription lets users purchase daily access to Moldflow Insight, Synergy, and Adviser with tokens, as opposed to a traditional subscription. Moldflow Flex provides a lower-cost option for users who don’t need to use the software every day. Anyone interested in Moldflow should contact Autodesk or their authorized reseller to speak with a sales associate and find the software version that best suits their needs.